Setup Cacao Accounting from the OCI image.
A OCI image is available to execute Cacao Accounting in containers based deployments, the OCI image is hosted in Quay .
Note
If you do not need a container based deployment you can install Cacao Accounting as a Python package from the package hosted at pypi .
Info
This guide uses podman and cockpit as reference, but you can use any tool you prefer to run
the Cacao Accounting OCI image like Docker CE.
Install the podman tool.
Podman is a container administration tool that organice groups of containerized
services in pods. Install podman in your server following these instructions:
sudo apt install -y podman
sudo dnf -y install podman
Cockpit Manager
Cockpit is a web based Linux administration tool that can manage containers and pod with a web interface, you can perform another administrative tasks :
sudo apt -y install cockpit-podman cockpit
sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
sudo dnf -y install cockpit-podman cockpit
sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
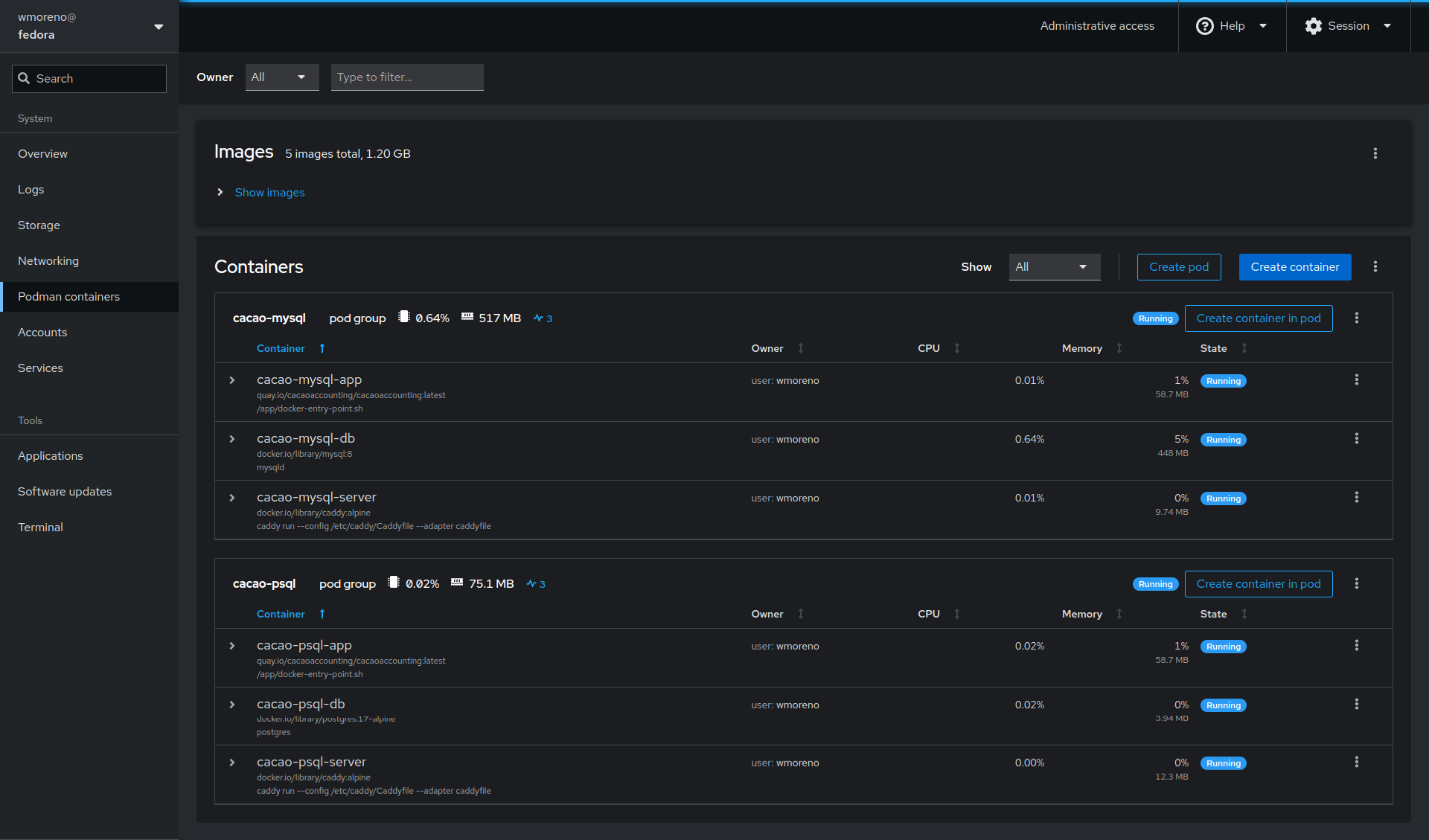
The next screenshot shows a Fedora Server host running multiple Cacao Accounting instances running in pods:
Execute the Cacao Accounting OCI imange.
To execute de Cacao Accounting OCI image you need to setup the following services:
- The Cacao Accounting wsgi app.
- A database service, you can use Postgresql or MySQL.
- A web server to handle users request, you can use Nginx, Caddy or any web server with proxy functionality.
- A optional Redis service for caching.
Info
This guide uses caddy because its simple configuration but Nginx is a another well documented web
server option.
Create a Caddy Server configuration file.
Similar to working with podman-compose it is recommended to create a directory to store the configuration files needed to
execute the services that a Cacao Accounting instance requires:
mkdir cacao-accounting-services
cd cacao-accounting-services
touch Caddyfile
Copy this base configuration to the Caddyfile:
:80 {
reverse_proxy localhost:8080
}
Note
Additional details to use Caddy as a proxy server is available in the Caddy website.
Create a pod to group Cacao Accounting services.
Note
You can create pod and services with the Cockpit Web UI interface, but for the brevety of this guide we will create the inicial services from the command line, once created the services can we handled with Cockpit.
Those are the commands required to setup a Cacao Accounting deploymen (chosee your prefered database service):
Tip
Do not copy and paste these commands directly, you can download a example script above and edit it with your prefered text editor.
podman pod create --replace --name cacao-mysql -p 9080:80 -p 9443:443 -p 9443:443/udp
podman volume create --ignore cacao-mysql-backup
podman run --pod cacao-mysql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-mysql-db \
--volume cacao-mysql-backup:/var/lib/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=cacaodb \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE=cacaodb \
-e MYSQL_USER=cacaodb \
-e MYSQL_PASSWORD=cacaodb \
-d docker.io/library/mysql:8
podman run --pod cacao-mysql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-mysql-server \
-v ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile:z \
-v caddy_data:/data \
-v caddy_config:/config \
-d docker.io/library/caddy:alpine
podman run --pod cacao-mysql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-mysql-app \
-e CACAO_KEY=nsjksAAA.ldknsdlkd532445yrVBNyrgfhdyyreys+++++ljdn \
-e CACAO_DB=mysql+pymysql://cacaodb:cacaodb@localhost:3306/cacaodb \
-e CACAO_USER=cacaouser \
-e CACAO_PSWD=cacaopswd \
-d quay.io/cacaoaccounting/cacaoaccounting:main
Download the base script for MySQL in the same directory of your Caddy file and edit.
Warning
Review the script before running it, it is adviced to setup a custom user and password for the
Cacao Accounting app.
$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cacao-accounting/cacao-accounting/refs/heads/main/docs/oci_files/mysql.sh
$ ls
mysql.sh Caddyfile
$ bash mysql.sh
podman pod create --replace --name cacao-psql -p 7080:80 -p 9444:443 -p 9444:443/udp
podman volume create --ignore cacao-postgresql-backup
podman run --pod cacao-psql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-psql-db \
--volume cacao-postgresql-backup:/var/lib/postgresql/data \
-e POSTGRES_DB=cacaodb \
-e POSTGRES_USER=cacaodb \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=cacaodb \
-d docker.io/library/postgres:17-alpine
podman run --pod cacao-psql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-psql-server \
-v ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile:z \
-v caddy_pg_data:/data \
-v caddy_pg_config:/config \
-d docker.io/library/caddy:alpine
podman run --pod cacao-psql --rm --replace --init --name cacao-psql-app \
-e CACAO_KEY=nsjksldknsdlkLKJ,dsljasfsadggfhh+++++++ASDhhf5325364dn \
-e CACAO_DB=postgresql+pg8000://cacaodb:cacaodb@localhost:5432/cacaodb \
-e CACAO_USER=cacaouser \
-e CACAO_PSWD=cacaopswd \
-d quay.io/cacaoaccounting/cacaoaccounting:main
Download the base script for Postgresql in the same directory of your Caddy file and edit.
Warning
Review the script before running it, it is adviced to setup a custom user and password for the
Cacao Accounting app.
$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cacao-accounting/cacao-accounting/refs/heads/main/docs/oci_files/psql.sh
$ ls
psql.sh Caddyfile
$ bash psql.sh
Allow Caddy Server to read the Caddyfile.
In Fedora, Rocky Linux, Alma Linux with active SELinux the :z option is required to grant the Caddy service read
access to the Caddyfile, other operative system like Debian or Ubuntu try :ro to grant read access to the process running
the container to the host file system.
Info
You can read more about containers file system access in this post: https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/container-permission-denied-errors
Allow access to restricted ports.
Warning
It is recomended to run podman containers as normal users (not root or sudo), running as root you can map your pod to ports under 1024.
Running podman as a not root user will no have access to map ports under 1024.
!! info
You can read more about containers port mapping in this post: [https://access.redhat.com/solutions/7044059](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/7044059)
Most of the time this is not a issue, but you can use redir to redirect traffic to restricted ports:
sudo dnf install redir
sudo redir -n -s :80 127.0.0.1:8080
You can run podman as root or with sudo to grant access to ports under 1024.